Possible optimisation: push down SORT and LIMIT nodes
| От | Christopher Wilson |
|---|---|
| Тема | Possible optimisation: push down SORT and LIMIT nodes |
| Дата | |
| Msg-id | BCCA73C2165E8947A2E786EC482564DE01301FB8F2@CCPMAILDAG03.cantab.local обсуждение исходный текст |
| Ответы |
Re: Possible optimisation: push down SORT and LIMIT nodes
|
| Список | pgsql-performance |
Hi all,
We have a query which is rather slow (about 10 seconds), and it looks like this:
select inventory.date, asset.name, inventory.quantity
from temp.inventory
left outer join temp.asset on asset.id = id_asset
order by inventory.date, asset.name
limit 100
The inventory table has the quantity of each asset in the inventory on each date (complete SQL to create and populate the tables with dummy data is below). The query plan looks like this (the non-parallel version is similar):
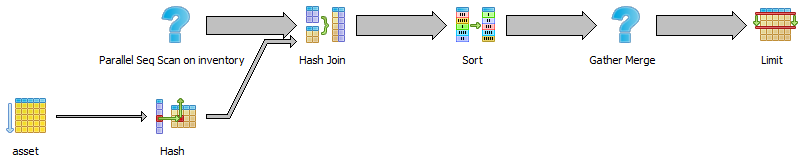
Or in text form:
Limit (cost=217591.77..217603.60 rows=100 width=32) (actual time=9122.235..9122.535 rows=100 loops=1)
Buffers: shared hit=6645, temp read=6363 written=6364
-> Gather Merge (cost=217591.77..790859.62 rows=4844517 width=32) (actual time=9122.232..9122.518 rows=100 loops=1)
Workers Planned: 3
Workers Launched: 3
Buffers: shared hit=6645, temp read=6363 written=6364
-> Sort (cost=216591.73..220628.83 rows=1614839 width=32) (actual time=8879.909..8880.030 rows=727 loops=4)
Sort Key: inventory.date, asset.name
Sort Method: external merge Disk: 50904kB
Buffers: shared hit=27365, temp read=25943 written=25947
-> Hash Join (cost=26.52..50077.94 rows=1614839 width=32) (actual time=0.788..722.095 rows=1251500 loops=4)
Hash Cond: (inventory.id_asset = asset.id)
Buffers: shared hit=27236
-> Parallel Seq Scan on inventory (cost=0.00..29678.39 rows=1614839 width=12) (actual time=0.025..237.977 rows=1251500 loops=4)
Buffers: shared hit=27060
-> Hash (cost=14.01..14.01 rows=1001 width=28) (actual time=0.600..0.600 rows=1001 loops=4)
Buckets: 1024 Batches: 1 Memory Usage: 68kB
Buffers: shared hit=32
-> Seq Scan on asset (cost=0.00..14.01 rows=1001 width=28) (actual time=0.026..0.279 rows=1001 loops=4)
Buffers: shared hit=32
Planning time: 0.276 ms
Execution time: 9180.144 ms
I can see why it does this, but I can also imagine a potential optimisation, which would enable it to select far fewer rows from the inventory table.
As we are joining to the primary key of the asset table, we know that this join will not add extra rows to the output. Every output row comes from a distinct inventory row. Therefore only 100 rows of the inventory table are required. But which ones?
If we selected exactly 100 rows from inventory, ordered by date, then all of the dates that were complete (every row for that date returned) would be in the output. However, if there is a date which is incomplete (we haven’t emitted all the inventory records for that date), then it’s possible that we would need some records that we haven’t emitted yet. This can only be known after joining to the asset table and sorting this last group by both date and asset name.
But we do know that there can only be 0 or 1 incomplete groups: either the last group (by date) is incomplete, if the LIMIT cut it off in mid-group, or its end coincided with the LIMIT boundary and it is complete. As long as we continue selecting rows from this table until we exhaust the prefix of the overall SORT which applies to it (in this case, just the date) then it will be complete, and we will have all the inventory rows that can appear in the output (because no possible values of columns that appear later in the sort order can cause any rows with different dates to appear in the output).
I’m imagining something like a sort-limit-finish node, which sorts its input and then returns at least the limit number of rows, but keeps returning rows until it exhausts the last sort prefix that it read.
This node could be created from an ordinary SORT and LIMIT pair:
SORT + LIMIT -> SORT-LIMIT-FINISH + SORT + LIMIT
And then pushed down through either a left join, or an inner join on a foreign key, when the right side is unique, and no columns from the right side appear in WHERE conditions, nor anywhere in the sort order except at the end. This sort column suffix would be removed by pushing the node down. The resulting query plan would then look something like:
Index Scan on inventory
SORT-LIMIT-FINISH(sort=[inventory.date], limit=100) (pushed down through the join to asset)
Seq Scan on asset
Hash Left Join (inventory.id_asset = asset.id)
Sort (inventory.date, asset.name)
Limit (100)
And would emit only about 100-1000 inventory rows from the index scan.
Does this sound correct, reasonable and potentially interesting to Postgres developers?
SQL to reproduce:
create schema temp;
create table temp.asset (
id serial primary key,
name text
);
insert into temp.asset (name) select 'Thing ' || random()::text as name from generate_series(0, 1000) as s;
create table temp.inventory (
date date,
id_asset int,
quantity int,
primary key (date, id_asset),
CONSTRAINT id_asset_fk FOREIGN KEY (id_asset) REFERENCES temp.asset (id) MATCH SIMPLE
);
insert into temp.inventory (date, id_asset, quantity)
select current_date - days, asset.id, random() from temp.asset, generate_series(0, 5000) as days;
Thanks, Chris.
Вложения
В списке pgsql-performance по дате отправления: